Understanding Needle Anxiety in the Context of Prescription Injection Weight Loss
Prescription injections have emerged as a pivotal tool in contemporary weight management protocols, especially with the rise of GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide. However, one frequently overlooked barrier to optimized adherence and therapeutic success is needle anxiety—an apprehension or fear of injections that compromises patient compliance. Recognizing the psychological and physiological underpinnings of needle anxiety is essential for clinicians and patients aiming to maximize the benefits of injectable weight loss medications.
Advanced Psychological and Physiological Mechanisms Behind Needle Anxiety
Needle anxiety is not merely a simple fear; it often involves complex conditioned responses influenced by prior traumatic experiences, anticipatory pain, and even vasovagal reactions. Neurobiological studies highlight the activation of the amygdala and insular cortex during needle exposure, which modulate fear and pain perception. This intricate interplay underscores the necessity for tailored interventions addressing both cognitive and somatic components to mitigate anxiety effectively.
What Are the Most Effective Evidence-Based Techniques to Manage Needle Anxiety in Injectable Weight Loss Therapy?
Clinical best practices recommend a multifaceted approach: cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques help reframe negative perceptions, while systematic desensitization gradually acclimatizes patients to injection procedures. Additionally, pharmacological adjuncts such as topical anesthetics reduce nociceptive input, and distraction techniques can attenuate acute stress responses during administration. Integrating patient education about the pharmacodynamics and benefits of the injections also empowers users, reducing apprehension rooted in uncertainty.
Optimizing Injection Techniques and Environment to Alleviate Needle Anxiety
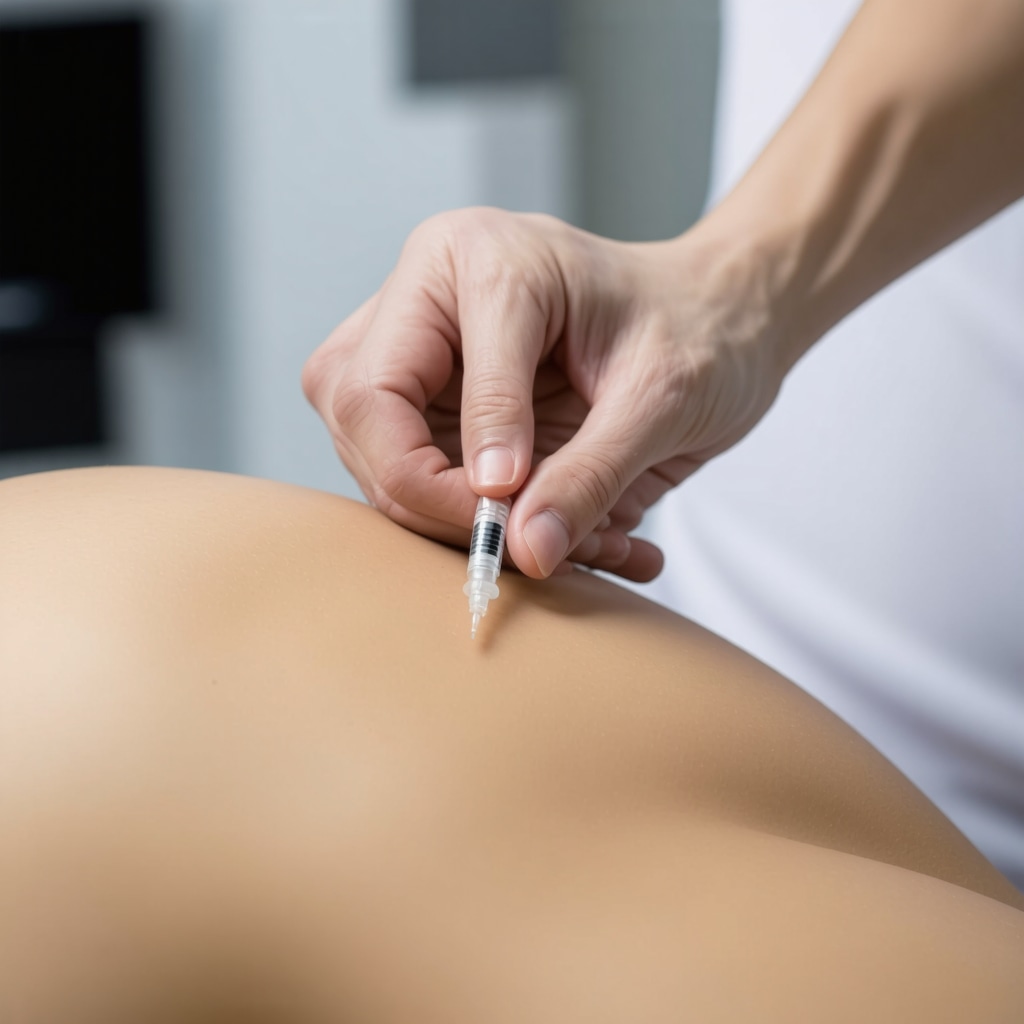
Technical proficiency in injection administration, including site rotation and proper needle disposal, contributes substantially to minimizing injection-related discomfort and psychological distress. Creating a calm, controlled environment with soothing stimuli can further alleviate anticipatory anxiety. For instance, scheduling injections at consistent times supports routine formation, reducing the unpredictability that often exacerbates fear.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Enhancing Compliance Through Anxiety Reduction
Physician-guided weight loss programs that incorporate regular counseling and monitoring have demonstrated higher adherence rates. Providers should proactively inquire about needle-related fears, offer personalized strategies, and recommend resources such as patient support groups or professional psychological services when necessary. The integration of such comprehensive support exemplifies medically supervised weight loss benefits, fostering trust and sustained engagement.
For a detailed exploration of needle anxiety avoidance techniques in prescription injection weight loss, as well as related expert insights, visit our in-depth resource.
Explore further expert-level discussions and contribute your professional insights on managing injection-related barriers in weight loss therapies by visiting our contact page.
According to a comprehensive review in the Journal of Pain Research, implementing multimodal approaches tailored to individual anxiety profiles significantly improves injection tolerability and patient outcomes, reinforcing the necessity of personalized care in this domain.
Integrating Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques to Enhance Injection Comfort
Beyond traditional cognitive-behavioral methods, incorporating mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) can significantly improve patient experiences during injectable weight loss therapy. These techniques actively engage the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing physiological markers of anxiety such as heart rate and muscle tension. For example, deep breathing exercises prior to injection can attenuate the acute stress response, making the procedure more tolerable and less intimidating.
Healthcare practitioners can guide patients through brief relaxation protocols immediately before administration, fostering a calmer mindset. This complements the pharmacological benefits of agents like semaglutide and tirzepatide by ensuring psychological barriers do not hinder adherence. Detailed guidance on integrating these relaxation methods with injectable treatments is available in our doctor-backed weight loss programs.
Technological Innovations: How Can Digital Tools Alleviate Needle Anxiety and Support Weight Loss Adherence?
Can Mobile Apps and Virtual Reality Simulations Revolutionize the Management of Needle Anxiety in Weight Loss Injections?
Emerging technology offers promising avenues to combat needle anxiety. Mobile applications designed to provide educational content, step-by-step injection tutorials, and anxiety tracking enable patients to gain confidence and autonomy. Furthermore, virtual reality (VR) exposure therapies create immersive environments where patients can gradually confront and desensitize their fear in a controlled, safe setting.
Evidence from a 2023 study published in Frontiers in Psychology demonstrates that VR interventions significantly reduce needle-related distress and improve compliance rates in chronic injection therapies. Integrating these digital tools with traditional medical guidance may transform patient engagement and outcomes in injectable weight loss treatments, making them indispensable adjuncts in modern clinical practice.
Optimizing Patient Education: Empowerment Through Knowledge and Skills
Patient education remains a cornerstone of mitigating needle anxiety. Detailed information about the pharmacological action, expected benefits, and potential side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists helps demystify the treatment. Demonstrations of proper injection techniques, including site rotation and safe disposal practices, increase patient confidence and reduce procedural errors that could provoke discomfort or complications.
Incorporating multimedia resources, such as instructional videos and interactive Q&A sessions, enhances understanding and retention. For clinicians aiming to personalize education effectively, resources like proper injection site care offer comprehensive guidance, ensuring patients are well-prepared and less anxious.
Tailoring Treatment Plans: The Intersection of Psychology and Pharmacology
Understanding individual patient profiles—including psychological predispositions, pain thresholds, and prior medical experiences—enables clinicians to customize treatment strategies. For example, gradually titrating dosages or selecting injection devices with finer needles can minimize discomfort. Concurrent psychological support, such as brief anxiety counseling or referral to specialists, can address deeper fears that interfere with adherence.
Such multidisciplinary approaches underscore the importance of medically supervised weight loss plans that holistically address both pharmacological and psychological dimensions. This synergy not only improves tolerability but also enhances long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction.
We invite readers and healthcare professionals to share their experiences and strategies for managing needle anxiety in injectable weight loss therapies in the comments section below. Engaging in this dialogue enriches community knowledge and fosters innovation in patient-centered care.
Neurofeedback and Biofeedback: Cutting-Edge Modalities for Managing Injection-Related Stress
Emerging neurotechnology offers promising adjunctive strategies for patients grappling with needle anxiety during injectable weight loss treatments. Neurofeedback, which trains patients to modulate their brainwave activity in real time, can reduce hyperactive fear responses by promoting relaxation-associated alpha and theta waves. Similarly, biofeedback devices monitor physiological markers such as heart rate variability and muscle tension, providing patients with immediate feedback that enables conscious downregulation of anxiety symptoms.
Integrating these modalities into pre-injection routines could empower patients to achieve greater autonomic stability, thereby attenuating the amygdala-driven fear circuits implicated in needle phobia. While still nascent in clinical application, pilot studies suggest that combining neurofeedback with cognitive-behavioral therapy may produce synergistic benefits in injection tolerance, warranting further exploration within weight loss pharmacotherapy frameworks.
Personalized Injection Devices: Customizing Comfort to Enhance Adherence and Outcomes
Technological advancements have expanded the spectrum of injection delivery systems tailored to reduce discomfort and needle fear. Pen injectors with ultra-fine needles, spring-loaded mechanisms, and hidden needle designs minimize visual and tactile triggers that exacerbate anxiety. Additionally, smart devices that provide real-time dosage confirmation and gentle injection speed control can reassure patients and improve their sense of control.
Clinicians should collaborate with patients to select devices that align with individual preferences and anxiety profiles, optimizing both psychological comfort and pharmacokinetic consistency. Such personalization exemplifies precision medicine principles applied beyond drug selection, extending into delivery mechanisms that directly influence therapeutic adherence and efficacy.
How Do Psychological Profiles Influence the Choice of Injection Techniques and Devices in Weight Loss Therapy?
Understanding a patient’s psychological makeup—including tendencies toward claustrophobia, tactile hypersensitivity, or prior injection trauma—can critically inform device selection and injection technique. For example, patients with high sensory sensitivity may benefit from slower injection speeds and devices designed to minimize pressure sensation, while those with avoidance behaviors might require more extensive desensitization protocols before transitioning to self-administration.
Assessment tools such as the Injection Phobia Scale-Anxiety (IPS-Anx) can quantify fear severity and guide clinicians in customizing interventions. This personalized approach not only enhances patient comfort but also mitigates risk of suboptimal dosing due to injection avoidance or improper technique.
Integrating Pharmacogenomics: Tailoring GLP-1 Agonist Therapies for Optimal Tolerability
Pharmacogenomic insights offer a frontier for reducing adverse effects that may compound injection-related anxiety. Genetic polymorphisms affecting drug metabolism, receptor sensitivity, and side effect susceptibility can influence both the physiological and psychological experience of injectable therapies.
For instance, variants in genes encoding GLP-1 receptors or enzymes involved in peptide degradation might affect therapeutic response or gastrointestinal side effects, which in turn impact patient willingness to continue injections. Future clinical protocols may incorporate genetic screening to personalize GLP-1 agonist selection and dosing, thereby optimizing tolerability and indirectly alleviating needle-related apprehension.
Authoritative sources like the Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase (PharmGKB) provide comprehensive data on gene-drug interactions relevant to weight loss pharmacotherapy, supporting evidence-based personalization.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration: The Synergistic Role of Psychologists, Pharmacists, and Physicians
Addressing needle anxiety in injectable weight loss therapy benefits enormously from a team-based care approach. Psychologists specialize in delivering anxiety management interventions and support cognitive restructuring, while pharmacists provide expertise on device selection and manage pharmacological adjuncts like topical anesthetics. Physicians oversee clinical monitoring and adjust treatment plans considering both psychological and physiological factors.
This coordinated care model facilitates early identification of barriers, continuous patient education, and rapid adaptation of strategies to optimize adherence and outcomes. Institutions embracing such integrative frameworks report higher patient satisfaction and improved long-term weight loss maintenance.
We encourage healthcare professionals to explore collaborative care models detailed in resources such as the American Journal of Preventive Medicine and to contribute to evolving best practices through interdisciplinary dialogue.
For practitioners seeking to deepen their expertise in managing injection-related anxiety and optimizing weight loss therapies, our upcoming webinars and workshops offer advanced training and case-based learning opportunities. Stay informed by subscribing to our expert newsletter.
Neurofeedback and Biofeedback: Harnessing Brain-Body Synchrony to Overcome Injection Stress
Cutting-edge neurotechnologies such as neurofeedback and biofeedback herald a new era in mitigating needle anxiety during injectable weight loss treatments. By training patients to consciously modulate brainwave frequencies—enhancing alpha and theta waves associated with relaxation—neurofeedback can attenuate hyperactive fear circuits within the amygdala. Concurrently, biofeedback devices provide real-time monitoring of physiological parameters like heart rate variability and muscle tension, empowering patients to implement effective anxiety reduction strategies on demand.
Integrating these modalities into pre-injection rituals fosters autonomic stability, easing the psychological burden of injections and potentially enhancing adherence. Though still emerging, preliminary studies underscore the transformative potential of combining neurofeedback with cognitive-behavioral frameworks to produce synergistic improvements in patient comfort and injection tolerability.
Personalized Injection Devices: Tailoring Delivery Systems to Psychological and Sensory Profiles
Advancements in injection technology offer bespoke solutions that reconcile pharmacokinetic efficacy with patient comfort and anxiety reduction. Devices featuring ultra-fine needles, spring-loaded mechanisms, and concealed needle designs minimize sensory triggers associated with needle phobia. Smart injectors with dosage confirmation and adjustable injection speeds further empower patients by fostering control and predictability.
Clinicians should assess psychological factors such as tactile hypersensitivity and avoidance tendencies to guide device selection, optimizing both the physical and emotional injection experience. This precision medicine approach extends beyond pharmacology to encompass delivery systems that directly influence therapeutic adherence and outcomes.
How Do Psychological Profiles Influence the Choice of Injection Techniques and Devices in Weight Loss Therapy?
Evaluating individual psychological constructs—ranging from claustrophobia to prior injection trauma—enables clinicians to customize injection protocols effectively. Tools like the Injection Phobia Scale-Anxiety (IPS-Anx) quantify fear severity, informing decisions on needle gauge, injection velocity, and the necessity of desensitization interventions. For example, patients exhibiting high sensory sensitivity may benefit from slower injection speeds and devices designed to minimize pressure sensations, whereas those with pronounced avoidance behaviors might require gradual exposure therapy prior to self-administration.
Such tailored strategies mitigate the risk of improper injection technique and improve dosing consistency, directly impacting therapeutic success.
Pharmacogenomics: Unlocking Genetic Insights to Optimize GLP-1 Agonist Therapy and Minimize Injection-Related Adversities
The integration of pharmacogenomic profiling into injectable weight loss regimens represents a frontier for enhancing tolerability and adherence. Genetic variants affecting GLP-1 receptor expression, peptide metabolism, and side effect susceptibility can modulate both physiological and psychological responses to treatment.
For instance, polymorphisms in genes such as GLP1R or DPP4 may influence gastrointestinal tolerability or efficacy, indirectly affecting patients’ willingness to maintain injection schedules. Incorporating genetic screening into clinical workflows facilitates personalized agent selection and dosing strategies, potentially reducing adverse effects that exacerbate needle anxiety.
Authoritative databases like the Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase (PharmGKB) provide comprehensive gene-drug interaction data critical for evidence-based precision medicine in obesity pharmacotherapy.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Synergizing Psychological, Pharmacological, and Technological Expertise for Optimal Patient Outcomes
Effective management of needle anxiety necessitates coordinated efforts among psychologists, pharmacists, and physicians. Psychologists deliver specialized anxiety interventions and cognitive restructuring, pharmacists guide device selection and recommend adjunctive pharmacological aids such as topical anesthetics, while physicians oversee therapeutic monitoring and tailor clinical plans.
This integrative care model enables early identification of psychological barriers, continuous patient education, and dynamic adaptation of treatment strategies. Institutions adopting this approach report superior patient satisfaction and improved long-term adherence to injectable weight loss therapies.
For further evidence-based guidance on collaborative models, consult the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, which elucidates best practices in interdisciplinary obesity management.
Healthcare professionals interested in advancing their expertise can access specialized webinars and workshops focusing on injection-related anxiety management and precision weight loss therapies by subscribing to our expert newsletter.
Engage With Advanced Insights to Transform Your Practice
We invite clinicians, researchers, and healthcare stakeholders to delve deeper into these innovative strategies and share their experiences in managing needle anxiety within injectable weight loss protocols. Your engagement fosters a collaborative knowledge base that propels patient-centered advancements and elevates therapeutic success.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Integrating Neurofeedback and Biofeedback Enhances Autonomic Regulation During Injection
Employing neurofeedback to modulate brainwave patterns alongside biofeedback monitoring of physiological markers offers a cutting-edge, patient-empowering approach to needle anxiety. This brain-body synchrony training can significantly reduce amygdala-driven fear responses, fostering a calmer state that promotes injection tolerance and sustained adherence in weight loss protocols.
Personalized Injection Devices Tailored to Psychological Profiles Optimize Patient Comfort
Selection of injection devices based on individual sensory sensitivity and anxiety profiles—using tools like the Injection Phobia Scale-Anxiety—enables clinicians to mitigate discomfort through fine needle gauges, spring-loaded mechanisms, or concealed needles. This customization not only eases needle fear but also improves pharmacokinetic consistency and therapeutic outcomes.
Pharmacogenomic Profiling Can Inform GLP-1 Agonist Selection to Minimize Adverse Effects
Incorporating genetic insights into treatment planning allows identification of polymorphisms affecting drug metabolism and receptor sensitivity, thereby tailoring GLP-1 agonist therapy to reduce side effects that exacerbate injection aversion. This precision medicine approach enhances tolerability and supports long-term engagement with injectable weight loss medications.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration is Essential for Holistic Needle Anxiety Management
Coordinated care involving psychologists, pharmacists, and physicians ensures comprehensive management of psychological barriers, device optimization, and pharmacological support. This synergy enables early identification of needle anxiety, patient-centered education, and dynamic adaptation of treatment strategies to maximize adherence and weight loss success.
Curated Expert Resources
Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase (PharmGKB): An authoritative database detailing gene-drug interactions relevant for tailoring GLP-1 receptor agonist therapies in obesity management, critical for clinicians pursuing precision medicine approaches.
American Journal of Preventive Medicine – Multidisciplinary Obesity Care Models: A key resource outlining best practices in interdisciplinary collaboration that enhances patient satisfaction and adherence in injectable weight loss treatment.
Frontiers in Psychology – Virtual Reality for Needle Anxiety: Provides evidence-based insights into immersive VR interventions reducing injection-related distress, offering innovative adjuncts to traditional anxiety management.
Injection Phobia Scale-Anxiety (IPS-Anx): A validated clinical tool to quantify needle fear severity, instrumental in customizing device selection and desensitization protocols.
eWeightLossTips Doctor-Backed Weight Loss Programs: Practical guidance on integrating psychological, pharmacological, and technological strategies for effective injectable therapy initiation and maintenance (link).
Final Expert Perspective
Needle anxiety represents a multifaceted challenge within prescription injection weight loss therapies, intricately woven into both psychological and physiological domains. Advanced interventions—from neurofeedback to personalized injection devices and pharmacogenomic-informed treatment plans—underscore the necessity of an individualized, multidisciplinary approach. Embracing these strategies not only alleviates injection-related distress but also significantly elevates adherence and therapeutic outcomes.
For clinicians and stakeholders committed to excellence in injectable weight loss care, engaging deeply with these insights and resources is crucial. We encourage you to explore further in-depth materials like our weekly injection weight loss guide and consider joining the dialogue on our contact page to share your expert perspectives and experiences.

As someone who has struggled with needle anxiety myself, I found this comprehensive overview incredibly insightful. The emphasis on combining psychological techniques like CBT and mindfulness with technological tools such as VR exposure is promising. I’ve experimented with deep breathing exercises before injections and noticed a real difference in my anxiety levels. I wonder how feasible it is to access these advanced technologies like neurofeedback or VR for the average patient, though. Do most clinics have the resources to incorporate such methods, or are they more suited for specialized centers? Personally, I believe that tailored patient education and simple relaxation techniques should be the first step, but it’s exciting to see these innovations potentially making a substantial impact. Has anyone here experienced or implemented neurofeedback or biofeedback in their practice? Would love to hear about real-world applications and patient feedback.