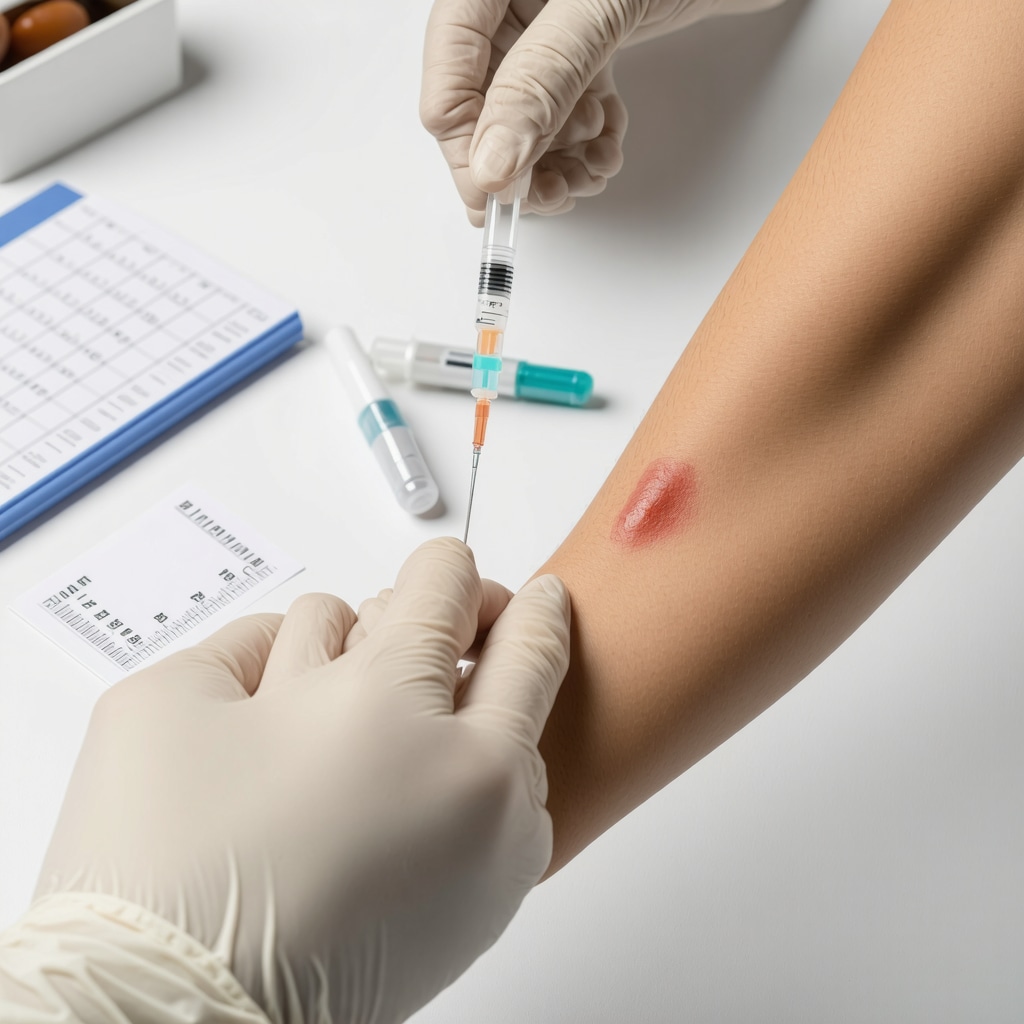
Understanding the Complexities of Injection Site Reactions in Semaglutide Therapy
Semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, has revolutionized weight management and glycemic control, yet its administration via subcutaneous injection presents unique challenges related to injection site reactions. These localized dermatological responses can impact patient adherence and therapeutic outcomes, necessitating an expert-level grasp of their pathophysiology and management strategies.
Mechanistic Insights into Injection Site Reactions: Beyond the Surface
Injection site reactions (ISRs) often manifest as erythema, swelling, pruritus, or nodules, reflecting complex immunological and tissue responses to the semaglutide molecule or its excipients. The inflammatory cascade involves mast cell degranulation, cytokine release, and localized edema, which can be exacerbated by improper injection techniques or repeated use of the same anatomical site. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for tailoring prevention and treatment protocols.
Expert Techniques to Minimize and Manage Injection Site Complications
Optimizing injection technique is paramount: rotating injection sites systematically between the abdomen, thigh, and upper arm reduces localized tissue trauma and immune sensitization. Utilizing proper needle length and angle, along with aseptic preparation, mitigates mechanical irritation. Post-injection care strategies, such as gentle massage and application of cold compresses, can attenuate inflammatory symptoms. In persistent or severe cases, topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be prescribed under medical supervision.
How Can Patients and Clinicians Collaborate to Address Injection Site Reactions Proactively?
Active patient education on injection site rotation and symptom monitoring is essential. Clinicians should implement regular injection site assessments and encourage patients to report adverse reactions promptly. Shared decision-making regarding dose adjustments or switching to alternative delivery methods may be warranted. Integrating these practices into comprehensive weight management plans enhances both safety and efficacy.
Integrating Semaglutide Injection Best Practices with Broader Weight Loss Strategies
Effective use of semaglutide goes beyond pharmacology; it involves harmonizing injection protocols with diet, exercise, and behavioral modifications. Resources such as doctor-backed advice on safe semaglutide use provide invaluable guidance to optimize outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
For further expert insights on minimizing injection-related side effects and mastering injection techniques, explore our detailed articles on avoiding injection site bruising and managing injection reactions effectively.
We invite healthcare professionals and experienced patients to share their insights and strategies in our community forum to foster a collaborative approach to semaglutide therapy optimization.
For authoritative clinical guidelines on managing injection site reactions in GLP-1 therapies, consult the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) review on GLP-1 receptor agonist adverse effects.
Personalizing Semaglutide Injection Protocols: The Role of Patient-Specific Factors
While standardized injection techniques form the backbone of minimizing injection site reactions (ISRs), individual patient factors such as skin type, subcutaneous fat distribution, and immune sensitivity significantly influence ISR risk and severity. For example, patients with thinner skin or lower fat mass may experience more pronounced tenderness or bruising. Age-related changes in skin elasticity and vascularity can also affect local tissue response. Tailoring needle length and injection depth accordingly reduces tissue trauma and inflammatory responses. Additionally, genetic predispositions towards hypersensitivity or autoimmune reactions may necessitate closer monitoring and alternative therapeutic approaches.
Engaging in a thorough pre-treatment assessment that incorporates these personalized factors can enhance patient comfort and adherence, thus improving overall therapy success. For those experiencing persistent ISRs, consultation with a healthcare provider to explore dosage adjustments or alternative GLP-1 receptor agonists with different excipient profiles is recommended.
Technological Innovations Enhancing Injection Safety and Comfort
Emerging technologies such as smart injection pens with dose tracking and ergonomic designs are revolutionizing patient experience. These devices offer precise dose delivery, minimize injection errors, and encourage consistent site rotation through digital reminders. Moreover, needle-free injection systems and microneedle patches are under investigation to reduce skin trauma and associated reactions, potentially expanding tolerability for patients with injection anxiety or heightened sensitivity.
Incorporating these innovations into clinical practice requires balancing cost, accessibility, and patient preferences, but they represent promising avenues to enhance the safety and efficacy of semaglutide therapy.
How Can Integrating Behavioral Interventions Amplify the Benefits of Semaglutide While Minimizing Adverse Injection Effects?
Behavioral strategies such as mindfulness-based eating, stress management, and structured physical activity not only potentiate weight loss outcomes but may also indirectly reduce the frequency and severity of injection site reactions. Stress reduction can modulate immune responses, potentially decreasing hypersensitivity reactions. Mindful eating supports appetite regulation enhanced by semaglutide, fostering sustainable lifestyle changes that complement pharmacotherapy.
Clinicians are encouraged to incorporate behavioral counseling into weight management plans, ensuring a holistic approach. Patients can benefit from resources that combine medication guidance with lifestyle education, such as doctor-approved advice on combining mindful eating and injections.
Expert Recommendations on Monitoring and Reporting Injection Site Reactions
Systematic monitoring of ISRs through patient diaries or digital health platforms enables timely identification and intervention. Recording parameters such as onset time, size, color, pain level, and duration of reactions facilitates pattern recognition and informs clinical decisions. Educating patients on distinguishing benign reactions from signs of infection or allergic responses is critical for safety.
Healthcare providers should establish clear communication channels, encouraging prompt reporting of severe or prolonged ISRs to prevent complications. This collaborative approach aligns with findings from the NCBI review on GLP-1 receptor agonist adverse effects, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and patient engagement in managing therapy-related side effects.
For a comprehensive guide on avoiding common injection side effects, visit our resource on tips for avoiding side effects with injectable weight loss treatments.
We invite readers to share their experiences and strategies for managing injection site reactions in the comments below and to explore additional expert guidance on safe semaglutide use and injection success to further enhance your therapeutic journey.
Harnessing Immunomodulatory Approaches to Mitigate Injection Site Hypersensitivity in Semaglutide Therapy
Injection site hypersensitivity reactions, while often mild, can escalate due to complex immune mechanisms including delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses. Cutting-edge immunomodulatory strategies focus on attenuating these localized immune responses without compromising systemic drug efficacy. For instance, pre-treatment with topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus has shown promise in reducing T-cell mediated inflammation at injection sites in select patients with recurrent ISRs. This approach demands careful clinical judgment, considering the balance between immune suppression and infection risk.
Furthermore, exploring the role of excipient selection is pivotal. Semaglutide formulations often include sodium phosphate or phenol, which may provoke irritant or allergic reactions. Developing excipient-free or hypoallergenic formulations could herald a new era of improved tolerability.
What Are the Latest Clinical Insights on Preventing Recurring Injection Site Nodules in Semaglutide Users?
Injection site nodules, characterized by firm, sometimes painful subcutaneous lumps, represent granulomatous inflammatory reactions often linked to repeated injections in the same area. Recent clinical trials emphasize the importance of meticulous site rotation combined with ultrasound-guided injection depth assessment to ensure delivery into appropriate subcutaneous tissue and avoid intradermal deposition which predisposes to nodule formation.
Additionally, intermittent use of low-dose systemic corticosteroids has been evaluated in refractory cases, though risk-benefit considerations remain paramount. Patient education on early recognition of nodules and prompt reporting is critical to prevent progression and optimize management.
Advanced Patient Monitoring Techniques: Leveraging Digital Health to Track Injection Site Reactions
Emerging digital health platforms empower patients and clinicians to capture detailed injection site data longitudinally. Applications equipped with image capture, symptom scoring, and automated alerts facilitate real-time ISR monitoring, enabling personalized adjustments in injection practices. Integration with wearable sensors that monitor skin temperature and local inflammation markers represents a frontier in proactive ISR management.
These technologies also foster enhanced patient engagement and adherence by providing immediate feedback and educational resources tailored to individual responses, thus bridging the gap between clinical visits.
Exploring the Biomechanics of Injection: Needle Design Innovations for Enhanced Tissue Compatibility
Needle technology has evolved beyond simple gauges; innovative designs now incorporate ultra-thin walls, silicone coatings, and variable bevel geometries to minimize tissue trauma and pain. Studies demonstrate that these refinements reduce microvascular damage and nerve irritation, directly correlating with decreased ISR incidence.
Moreover, the advent of microneedle arrays promises minimally invasive delivery, potentially circumventing traditional injection site complications altogether. While still investigational for semaglutide, these devices may transform administration paradigms by enabling painless, self-administered dosing with superior patient acceptance.
How Does Skin Microbiome Variation Influence Semaglutide Injection Site Reaction Risk?
Recent research highlights the skin microbiome’s role as a modulator of local immune responses and barrier integrity. Dysbiosis or pathogenic colonization at injection sites can amplify inflammatory cascades, escalating ISR severity. Personalized skincare regimens incorporating prebiotics, probiotics, or targeted antimicrobial interventions before and after injection may mitigate these effects.
Clinical trials investigating microbiome modulation as part of comprehensive ISR prevention strategies are underway, signaling a novel dimension of personalized semaglutide therapy.
For clinicians and patients seeking to deepen their understanding of injection site reactions and optimize semaglutide therapy, we recommend reviewing the detailed clinical analyses presented by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) on GLP-1 receptor agonist adverse effects, which provide authoritative guidance grounded in the latest evidence.
Engage with our expert community to share experiences, discover innovative solutions, and stay abreast of emerging best practices in semaglutide administration and injection site management.
Immunomodulatory Frontiers in Managing Semaglutide Injection Site Hypersensitivity
Beyond conventional anti-inflammatory approaches, leveraging targeted immunomodulation offers unprecedented control over injection site hypersensitivity reactions (ISRs) associated with semaglutide therapy. The application of topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus, selectively downregulates T-cell mediated inflammation, presenting a nuanced option for patients with recurrent localized immune responses. This advanced immunotherapeutic strategy requires precision and vigilant clinical oversight to mitigate infection risks while preserving drug efficacy.
What Are the Latest Clinical Insights on Preventing Recurring Injection Site Nodules in Semaglutide Users?
Clinicians now emphasize the criticality of ultrasound-guided injection depth assessment to ensure subcutaneous delivery and prevent intradermal deposition, a known precipitant of granulomatous nodule formation. Meticulous site rotation protocols, combined with patient education on early nodule recognition, form the cornerstone of effective prevention. Emerging evidence has also explored intermittent low-dose systemic corticosteroid regimens for refractory nodules, although this demands judicious risk-benefit analysis.
Decoding the Skin Microbiome’s Role in Injection Site Reactions: A Personalized Perspective
Recent advances in dermatological immunology reveal the skin microbiome as a pivotal modulator of local inflammatory milieu post-injection. Variations in microbial communities can predispose to heightened immune activation or impaired barrier function, exacerbating ISRs. Integrating personalized skincare—employing prebiotics, probiotics, and selective antimicrobials—before and after semaglutide administration is an emerging paradigm aimed at microbiome stabilization and ISR mitigation.
Ongoing clinical trials are investigating these microbiome-targeted interventions, heralding a future where injection site reaction management transcends symptomatic treatment to encompass microbial ecosystem modulation.
Technological Innovations: Transforming Injection Safety with Digital and Mechanical Advances
The integration of digital health platforms facilitates sophisticated ISR monitoring through features like symptom scoring, photographic documentation, and real-time clinician alerts, enabling personalized intervention strategies. Wearable biosensors capable of detecting localized inflammation markers and skin temperature fluctuations represent the vanguard of proactive ISR management, offering continuous data streams that inform clinical decision-making.
Parallel advancements in needle engineering—incorporating ultra-thin walls, silicone coatings, and innovative bevel geometries—minimize tissue trauma and nociceptive signaling. The investigational application of microneedle arrays promises near-painless semaglutide delivery with a substantial reduction in localized adverse reactions, potentially revolutionizing patient adherence and comfort.
For a comprehensive review of the latest evidence and expert consensus on GLP-1 receptor agonist adverse events, including injection site reactions, the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) provides an authoritative resource.
Engage with our expert community today to explore these advanced insights, share your clinical experiences, and stay abreast of evolving best practices that optimize semaglutide therapy outcomes while minimizing injection site complications.

Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Understanding the Immunological Nuances Behind Injection Site Reactions
Injection site reactions (ISRs) extend beyond mere irritation; they represent a complex interplay of localized immune activation involving mast cells, T-cell mediated delayed hypersensitivity, and cytokine cascades. Recognizing this layered immunopathology is essential for clinicians aiming to tailor interventions — from topical immunomodulators to strategic site rotation — that address the root causes rather than just symptoms.
Personalization of Injection Technique Based on Patient-Specific Factors
Standardized injection protocols provide a foundation, but optimizing needle length, injection angle, and anatomical site selection according to individual skin thickness, adipose distribution, and immune sensitivity significantly reduces ISR risk. This precision approach enhances patient comfort and adherence, underscoring the importance of personalized care pathways in semaglutide administration.
Leveraging Digital Health Technologies to Elevate ISR Monitoring and Management
Cutting-edge digital platforms incorporating photographic documentation, symptom scoring, and wearable biosensors enable real-time tracking of ISRs. These tools empower both patients and clinicians with actionable data to anticipate, mitigate, and rapidly respond to adverse reactions, facilitating a dynamic and personalized therapeutic experience.
Innovations in Needle Design and Delivery Systems to Minimize Tissue Trauma
Advancements such as ultra-thin wall needles, silicone coatings, and microneedle patches reduce mechanical irritation and nociceptive signaling at injection sites. While still emerging for semaglutide, these technologies promise to transform administration by enhancing patient comfort and reducing ISR incidence, potentially improving long-term adherence.
Integrating Skin Microbiome Modulation into ISR Prevention Strategies
Emerging evidence highlights the skin microbiome’s role as a critical modulator of local immune responses post-injection. Personalized skincare interventions employing prebiotics, probiotics, or targeted antimicrobials before and after semaglutide administration represent a promising frontier to stabilize microflora and reduce inflammatory reactions at injection sites.
Curated Expert Resources
National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Review on GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Adverse Effects: This comprehensive review offers authoritative, up-to-date insights into the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and management strategies of injection site reactions and other adverse events associated with GLP-1 therapies, making it indispensable for clinicians and researchers alike.
Doctor-Backed Advice on Safe Semaglutide Use (eWeightLossTips.com): This resource synthesizes practical clinical recommendations on injection techniques, site rotation, and adverse effect management, supporting both patients and healthcare providers in optimizing semaglutide therapy.
Advanced Injection Site Care and Side Effect Mitigation (eWeightLossTips.com): Focused on recognizing and addressing injection site complications, this detailed guide enhances understanding of symptomatology and evidence-based interventions.
Expert Community Forums on Semaglutide Therapy: Engaging with peer and professional communities provides real-world insights, shared best practices, and emerging innovations in managing injection site reactions and improving adherence.
Emerging Research on Skin Microbiome and Injection Site Immunity: Scholarly articles and clinical trials exploring microbiome modulation offer a glimpse into next-generation strategies for ISR prevention and personalized dermatologic care.
Final Expert Perspective
Mastering the management of semaglutide injection site reactions demands a synthesis of immunological understanding, personalized injection techniques, and the judicious application of emerging technologies. By embracing a patient-tailored approach that incorporates immunomodulatory strategies, digital monitoring tools, and advances in needle design, healthcare professionals can significantly enhance therapeutic outcomes and patient satisfaction. The integration of skin microbiome considerations further enriches this multifaceted strategy, heralding a new paradigm in injection site care.
For those committed to optimizing semaglutide therapy, continuing education through authoritative resources and active engagement within expert communities is vital. Explore comprehensive guidance on safe semaglutide use and injection success and deepen your expertise with related insights on avoiding injection site bruising and doctor-backed injection strategies. Engage with our expert community to share your experiences and contribute to advancing best practices in semaglutide administration.